3D Dental Scans vs. X-Ray: Important Differences to Know
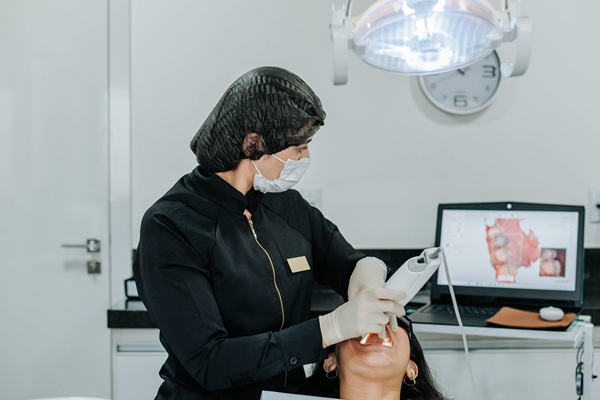
Staying informed about dental imaging options empowers patients to make better decisions about oral health. A 3D dental scan and a traditional dental X-ray both help dentists visualize structures beneath the surface, but these tools function differently and offer unique advantages. Understanding how they compare may help patients feel more confident during exams and treatment planning.
What is a 3D dental scan?
A 3D dental scan uses cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) to capture detailed, three-dimensional images of the teeth, bone, sinuses, and jaw joints. Unlike traditional X-rays, which provide only flat, two-dimensional views, 3D dental scans offer a more complete view of the oral and maxillofacial structures from multiple angles. This technology is especially useful for procedures such as dental implants, root canal evaluations, and bone density assessments.
Since the scan delivers highly precise images, a dentist can evaluate structures with greater accuracy. A 3D dental scan is often crucial for planning surgical treatments or diagnosing complex conditions that standard X-rays may not fully reveal.
How traditional X-rays work
Traditional X-rays use a small dose of radiation to capture two-dimensional images of the teeth and surrounding bone. They are quick, painless, and suitable for routine dental visits. Dentists use bitewing, panoramic, and periapical X-rays to identify cavities, infections, or changes in bone density over time. While useful for general exams and early detection, traditional X-rays offer less detail than 3D scans. They cannot show cross-sectional images or give exact measurements of bone or tissue depth.
Comparing use cases
Each imaging tool has its ideal purpose. For example, a 3D dental scan is well-suited for advanced diagnostics, such as detecting impacted teeth, cysts, or structural abnormalities. Traditional X-rays, on the other hand, are best used during regular checkups to monitor teeth and detect decay or minor issues. Choosing between these methods depends on the nature of the concern. A general dentist may recommend one over the other depending on the level of detail needed for accurate planning or diagnosis.
Differences in accuracy and detail
A key difference between a 3D dental scan and a traditional X-ray lies in the level of precision. A 3D scan allows the dentist to view the anatomy from all directions, reducing guesswork in treatments such as implant placement or surgical extractions. It also improves safety by helping avoid nerves and blood vessels during procedures.
Traditional X-rays offer a simpler and faster approach but may not capture enough information when conditions involve the jaw, sinuses, or deep-rooted infections. This limitation could lead to delays in treatment or the need for additional imaging.
Safety considerations
Both types of imaging involve radiation, but modern technology significantly reduces exposure. A 3D dental scan delivers slightly more radiation than a standard X-ray, though it remains within safe diagnostic limits. Dentists use protective measures and only recommend imaging when clinically necessary.
Call us for more information
Choosing the right imaging method depends on the treatment plan and the condition. Our general dentist can explain whether a 3D dental scan or a traditional X-ray provides the most helpful information for each case. For more information or to schedule a visit, contact our office today.
Request an appointment here: https://www.friendlydentaltemecula.com or call Friendly Dental Center at (951) 225-4888 for an appointment in our Temecula office.
Check out what others are saying about our services on Yelp: Read our Yelp reviews.
Related Posts
All-on-4 implants represent a modern approach to full-arch tooth replacement, offering stability, efficiency, and long-term oral function. This treatment concept has transformed restorative dentistry by combining surgical precision with prosthetic innovation. The following five facts explain why this solution continues to gain attention among dental professionals and patients seeking comprehensive tooth replacement options.All-on-4 implants rely…
A dental bridge can simplify tooth replacement so patients can restore their smiles. However, many are nervous about getting the bridge because they know that it involves modifying the other teeth near the gap.Fortunately, the dental bridge procedure is quite simple and is usually performed on an outpatient basis. This means you can go home…
Missing teeth can significantly impact your oral health, appearance, and confidence. Fortunately, teeth replacement options like dental bridges can help restore your smile. Dental bridges are prosthetic devices designed to bridge gaps made by one or more missing teeth, repairing the function and appearance of your smile.Dental bridges are fixed dental restorations that replace missing…
Dental bridges help restore smiles and maintain oral health by replacing missing teeth. Understanding the different types of dental bridges can help you choose the right solution for tooth loss. The following blog covers the four main types of dental bridges and their features.Traditional dental bridges are among the most common options for replacing missing…
